If you have ever wondered what a rectifier on a motorcycle is, you’re not alone. This key component of a motorcycle’s charging system plays a significant role in maintaining the performance of your ride. This article aims to shed light on the function and significance of a motorcycle rectifier.
Quick Overview of A Motorcycle’s Charging System
A motorcycle’s charging system is a vital part of its overall functioning. It consists of several components, including the alternator, battery, and the subject of our discussion today – the rectifier.
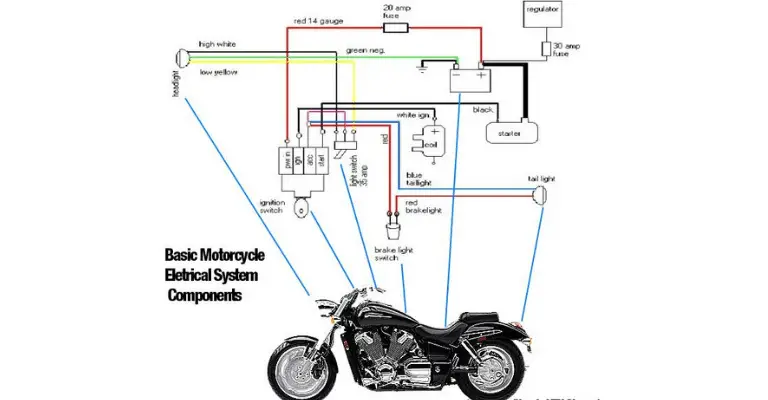
The charging system’s primary role is to generate power for the motorcycle’s electrical components and to maintain the battery’s charge level.
So, What Is A Rectifier On A Motorcycle? What Does It Do?
Also known as a voltage regulator, a motorcycle rectifier is a critical component of the bike’s charging system. It primarily serves two functions – rectification and regulation. Rectification involves converting alternating current (AC) produced by the alternator into direct current (DC) required by the motorcycle’s electrical system. Once the AC power is converted to DC, the rectifier’s regulation function comes into play, maintaining the voltage within the safe operating range of around 14.5 volts.
Overview of The Differences Between AC and DC Voltage
Before we delve deeper into the rectifier’s operation, it’s crucial to understand the difference between AC and DC voltage. Alternating current (AC), as the name suggests, alternates its direction periodically. On the other hand, direct current (DC) flows in a single direction. Most electronic devices, including motorcycles, require DC power to operate smoothly.
Are There Different Types of Rectifiers?
Yes, indeed. The two main types of rectifiers found in most motorcycles are the Permanent Magnet Rotor Alternator (PMR) and the Field Control Type (FCT). The PMR type possesses permanent magnets that rotate around the engine, whereas the FCT type features a ‘field’ or ‘exciter’ coil that becomes magnetized once supplied with power from the regulator.
Diodes, Mosfets, Etc,.
Diodes and MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor) are other key components of a rectifier. Diodes allow current to flow in one direction, aiding in the conversion of AC to DC. MOSFETs, on the other hand, are used in modern rectifiers to regulate voltage more efficiently, contributing to longer battery life and better electrical system performance.
Check out this video to learn more:
[su_youtube_advanced url=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3T4fYf-JSHs” title=”This is a video titled ‘Compare Voltage Regulator: Diode v MOSFET’”]
Can A Motorcycle Run Without A Rectifier?
Theoretically, a motorcycle could operate without a rectifier, but it would be for a limited duration. This is because the rectifier plays an integral role in converting AC power to DC power and maintaining the voltage within a safe range. Without a functioning rectifier, the battery won’t receive the proper charging voltage, leading to a discharged or weak battery over time. This condition, known as ‘total-loss ignition,’ will eventually result in the engine stalling.
Do Rectifiers Go Bad?
Yes, rectifiers can go bad. Overheating due to poor placement or weak connections with the battery can cause a rectifier to fail. The battery relies on a sturdy ground connection for voltage. If the connection is bad, the rectifier will run hotter than usual, leading to potential failure.
Bad Rectifier Symptoms To Look Out For
Recognizing the signs of a failing rectifier can save you from more serious problems down the line. Some indicators that your rectifier might be malfunctioning include:
Dim Lights
If your bike’s headlights are dim or flickering, it might indicate an issue with the rectifier. This is because the lights are connected to the alternator, and if the battery isn’t receiving enough charge from the alternator and rectifier, it will decrease the power input to the lights.
Overly Bright Lights
On the other hand, if your lights are excessively bright, it may mean that the rectifier is failing to regulate the voltage, leading to an overcharge of the battery.
Difficulty Running
If your motorcycle has trouble running or displays reduced power, it might be due to a failing rectifier. The rectifier’s role in maintaining the bike’s electrical system means that any malfunction could significantly impact the bike’s performance.
Reduced Power
A significant drop in your motorcycle’s power could signal a problem with the rectifier. This is due to the rectifier’s responsibility in maintaining the bike’s electrical system, and any malfunction could significantly impact the bike’s performance.
Complete Stalling
If your motorcycle stalls completely, it could be due to a completely failed rectifier. In such a case, the battery would not receive the necessary DC voltage for operation, leading to a complete shutdown.
Won’t Start
Similarly, if your motorcycle refuses to start, it might be due to a bad rectifier. An insufficiently charged battery won’t have the necessary power to kick-start the motorcycle.
How To Identify A Bad Rectifier
If you’re experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, it’s time to test your rectifier. Using a multimeter, you can check the output voltage. If the voltage reads below 13 volts or above 17 volts, it could indicate a faulty rectifier.
Can You Fix It Yourself?
While it’s possible to replace a bad rectifier yourself, it’s crucial to understand the process and risks involved fully. If you’re not confident in your technical abilities, it’s always best to consult a professional mechanic.
How To Test A Rectifier With A Multimeter (Step-By-Step Guide)

Testing a rectifier with a multimeter is relatively straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Start by disconnecting the rectifier from your bike.
- Set the multimeter to diode function.
- Connect the positive lead of the multimeter to the positive diode of the rectifier.
- Connect the negative lead of the multimeter to the stator inputs.
- Repeat the process with the negative diode.
If the voltage reading is lower than 13 volts or higher than 17 volts, it points to a faulty rectifier.
What To Know About Diagnosing and Replacing a Rectifier?
Diagnosing and replacing a rectifier requires a basic understanding of motorcycle mechanics. If you’re unsure about the process, it’s best to seek professional help. Keep in mind that a faulty rectifier could cause additional problems with your motorcycle’s electrical system, so it’s important to address the issue promptly.
Recap of Important Points
In summary, a rectifier is an essential component of a motorcycle’s charging system, responsible for converting AC power to DC power and regulating the voltage. While a motorcycle can run without a rectifier for a short period, a malfunctioning or failed rectifier can lead to a host of problems, from dim lights to a stalled engine. Recognizing the symptoms of a bad rectifier and knowing how to test it can help you maintain your motorcycle’s performance and prevent more serious issues down the line.
Tips for Safety and Proper Diagnosis and Installation
When diagnosing or replacing a rectifier, always prioritize safety. Ensure you’re using the right tools, and don’t attempt to work on your motorcycle if you’re unsure about the process. Remember, when in doubt, it’s always safer to consult a professional mechanic.
Wrapping Up
Understanding the role of a rectifier in a motorcycle’s charging system is crucial for maintaining your bike’s performance and longevity. By recognizing the symptoms of a faulty rectifier and knowing how to test it, you can prevent potential issues and ensure a smoother, safer ride.