Picture this: You’re about to head out on a much-anticipated ride, the weather’s perfect, your mood’s on point, but there’s just one tiny hiccup — your motorcycle cranks but refuses to start. Sounds familiar? Ah, the classic ‘no spark’ conundrum! It’s a dilemma that has baffled many a biker, from novices to seasoned riders. But before you let this setback kill your vibe, we’ve got your back.
Dive into this guide to understand, diagnose, and conquer the ‘no spark‘ mystery that’s messing with your ride. From breaking down the intricate world of your bike’s electrical system to hands-on troubleshooting steps, we’re about to turn you into a motorcycle electrical maestro. So, strap in, and let’s electrify that journey back to the open road!
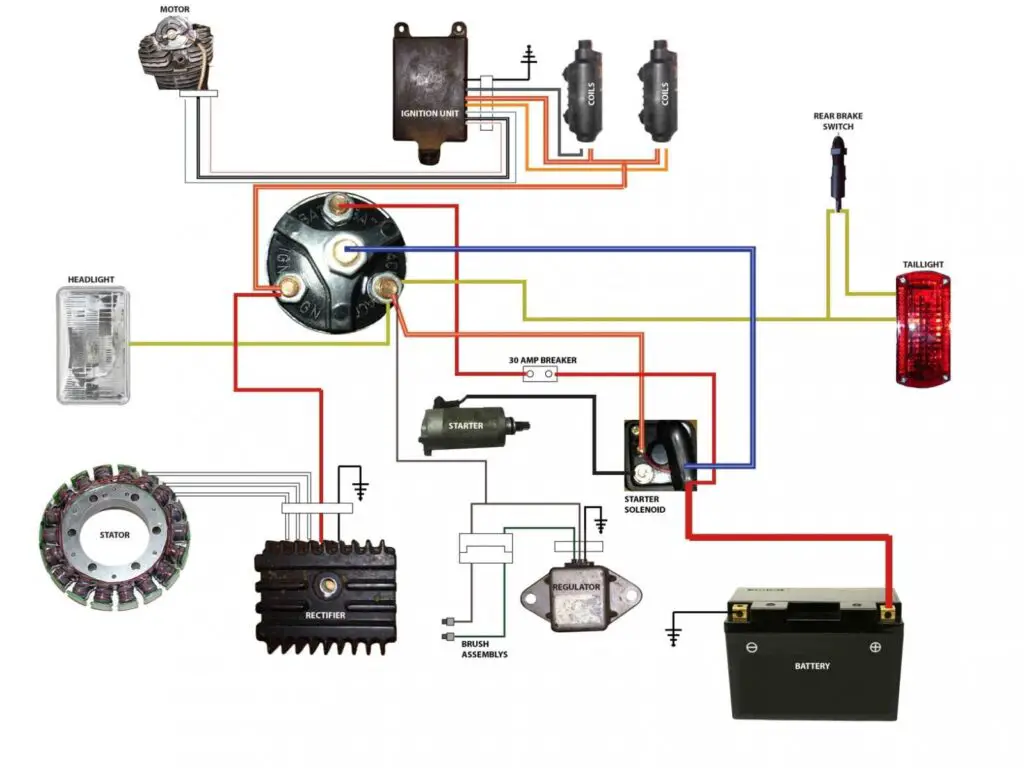
Brief Overview of The Electrical System Components on Motorcycles
A motorcycle’s electrical system is a complex network of components working in harmony to ensure a smooth ride. Here’s a quick rundown of the key players:
- Battery: Powers the electrical system and provides the initial spark to start the engine.
- Ignition Switch: Activates the electrical system when you turn the key.
- Fuses: Protect the electrical circuits from damage due to excess current.
- Wiring: Connects all electrical components together, allowing current to flow.
- Coil: Transforms the battery’s low voltage to the high voltage required to generate a spark at the spark plug.
- Spark Plug: Generates a spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the engine.
- Regulator/Rectifier: Controls the voltage produced by the stator, converts it from AC to DC, and charges the battery.
Brief Overview of Ignition Components on A Motorcycle
The ignition system is a subset of the electrical system, focused on creating the spark needed to run the engine. Its main components are:
- Ignition Switch: This is where you insert your key to start the bike.
- Spark Plug: Creates a spark to ignite the air-fuel mixture in the engine.
- Ignition Coil: Acts as a transformer to boost the battery’s low voltage to the high voltage needed to create a spark.
- CDI (Capacitor Discharge Ignition) Module: Controls the timing and intensity of the spark.
- Pick-up Coil/Pulse Generator/Source Coil: Provides the timing signal for the ignition system.
What Can Lead To A No Spark Condition On A Motorcycle?
Several factors can cause a no spark condition on a motorcycle. Here are the most common ones:
- Faulty Spark Plug: The spark plug might be worn out, fouled, or have a broken insulator.
- Bad Ignition Coil: The coil could be failing to step up the voltage to the required level.
- Defective CDI Module: The CDI controls the spark’s timing and intensity. If it’s faulty, no spark will be produced.
- Worn-out Pick-up Coil: This component generates the timing signal for the ignition system. If it’s defective, the spark could be off-time or non-existent.
- Damaged Wiring or Connectors: Any broken or loose connections can disrupt the flow of electricity, preventing a spark.
- Battery Issues: A weak or dead battery may not supply enough power to generate a spark.
- Faulty Safety Switches: If the kickstand, neutral, or clutch switches malfunction, they can prevent the bike from starting.
Related: Why Is My Motorcycle Losing Power When Accelerating?
So, What Do You Do When Your Motorcycle Has No Spark?
Before you start replacing parts, it’s essential to diagnose the issue methodically. The key is patience and open-mindedness. Don’t rush to conclusions based on hearsay or assumptions. Make sure to test each component individually to pinpoint the root cause.
How To Test Each Part Of The Electrical System
Here are step-by-step instructions to check each part of the electrical system:
- Battery: Check if it’s fully charged and the terminals are clean. Use a multimeter to measure the voltage between the positive and negative terminals. It should read above 12.4V, closer to 12.6V.
- Fuses: Inspect the main fuse and others for any signs of burning or damage.
- Wiring: Visually inspect the wiring for any damage. Clean all the connectors by unplugging them and spraying with WD40. Apply some dielectric grease to prevent future corrosion.
- Ignition and Kill Switch: Make sure both are in the ‘ON’ position. Use a multimeter to check for continuity between the terminals.
- Safety Switches: Check the kickstand, neutral, and clutch switches. They shouldn’t prevent the bike from starting when in the correct state.
Steps for Repairs as Necessary
If you found any issues during your electrical system inspection, here are some corrective steps:
- Battery: If it’s not fully charged, hook it up to a charger overnight. If the terminals are dirty, clean them with a baking soda solution and sandpaper.
- Fuses: Replace any burnt-out fuses. If you find a burnt fuse, investigate the cause to prevent future occurrences.
- Wiring: If there’s any damage, replace the affected section or the faulty connector.
- Switches: If any switch is not working correctly, clean it and try again. If it still doesn’t work, replace it.
How To Test The Ignition System
Once you’ve checked the electrical system, it’s time to focus on the ignition system. Here are the steps:
- Spark Plug: Remove the spark plug cap and wire from the spark plug. Hold the threaded part against the engine to short the plug. Briefly push the starter. You should see a bright blue or white spark.
- Ignition Coil: Disconnect the spark plug wire from the coil and measure the resistance between the terminals using a multimeter. The readings should fall within the acceptable range mentioned in your service manual.
- CDI Module: There’s no way to properly test the CDI. The best option is to replace it with a known good one and see if that fixes the problem.
- Pick-up Coil: Measure the resistance between the two wires going to the pick-up coil. It should be within the specified range in your service manual.
Steps to Repair When Necessary
If any of the ignition components are defective, here are some steps to fix them:
- Spark Plug: If there’s no spark or a weak spark, replace the spark plug.
- Ignition Coil: If the primary or secondary resistance is outside the acceptable range, replace the coil.
- CDI Module: If replacing the CDI module fixes the no spark condition, keep the new one.
- Pick-up Coil: If the resistance is not within the specific range, replace the pick-up coil.
Practical Tips for Maintaining Your Electrical System
To avoid future no spark situations, follow these maintenance tips:
- Regularly check your battery’s charge and ensure the terminals are clean.
- Keep the wiring in good condition. Use dielectric grease on connectors to prevent corrosion.
- Regularly inspect and replace spark plugs as per your service manual.
- Check the fuses and replace any that are damaged.
- Regularly inspect and clean or replace the ignition coil, CDI, and pick-up coil as necessary.
Recap of Important Points
A no spark condition on your motorcycle can be frustrating, but with patience and systematic troubleshooting, you can solve the problem. Remember to check each component of the electrical and ignition systems individually. Regular maintenance can help prevent such issues in the future. Now, take a deep breath, grab your tools, and let’s get your motorcycle sparking again!