Harley Davidson engines have long been the heart and soul of the iconic motorcycles that bear their name. From the rumble of an idle to the roar on the open road, the different engine sizes—specifically the 88, 96, and 103 cubic inches—have fueled discussions amongst enthusiasts. This detailed exploration aims to dissect the nuances that define the performance and durability of these legendary engines, delivering an authoritative Harley Davidson engine comparison. Understanding the subtle yet significant differences in a Harley 88 vs 96 vs 103 shootout, is essential for both seasoned riders and curious newcomers alike. As we delve into each engine’s characteristics, we’ll consider Harley engine specifications that highlight the evolution of these venerable powerplants.
Easy navigation:
– Harley 88 vs 103: Performance, Power, Upgradability and More
Key Takeaways
- The Twin Cam 88 engine set a high standard for reliability, which later engines built upon.
- Each subsequent engine size, from the 96 to 103, offered incremental increases in more torque, power, and general performance.
- Hydraulic tensioners, introduced in 2007, marked a significant improvement in engine longevity.
- Upgrades and modifications can substantially enhance engine performance, particularly for the 103 cubic inch models.
- Despite the evolution, rider preference plays a significant role in which engine is the right fit for individual needs.
- Understanding each engine’s nuances can lead to better maintenance decisions and more enjoyable riding experiences.
Understanding Harley Davidson Engine Evolution
The legacy and prowess of Harley Davidson’s engines have been a hallmark of the brand’s commitment to performance and quality. With the advent of each new engine size, from the esteemed Harley 88 to the potent Harley 103, both the casual rider and the performance enthusiast have witnessed a fascinating evolution in motorcycle engineering. Key developments in Harley engine upgrades and enhancements in Harley davidson engine specifications have been central to this enduring story.
The Emergence of the Twin Cam 88 Engine
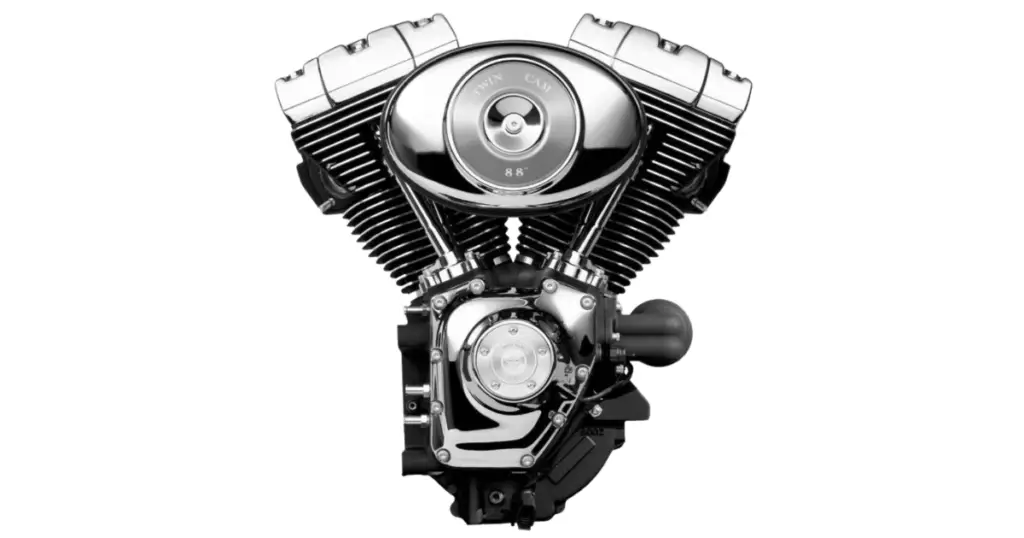

Introduced in the late 1990s, Harley-Davidson’s Twin Cam 88 engine set a new standard in robustness and reliability. Early models were heralded for their high-quality crank mechanisms and durable Timken bearings—a testament to Harley-Davidson’s engineering focus. Despite pressures to reduce manufacturing costs, significant improvements like hydraulic tensioners, introduced in 2007, bolstered the Harley engine sizes explained as benchmarks of dependability.
Read more here: Is The Twin Cam 88 A Good Motor? Yes and No (Here’s Why)
From 88 to 96: A Shift Toward Greater Power
As riders sought more power and torque, Harley-Davidson responded by increasing engine displacement with the Harley 96. Debuting in the late 2000s, the 96 cubic inch engines were a nod to the demands for Harley Davidson performance, engaging a broader spectrum of motorcycle aficionados. The conventional Harley 88 engines, known for their lively response, were now complemented by the heftier 96 models that, with stage 2 modifications, unleashed a new realm of power and adaptability.
Read more here:
– Harley 88 vs 107: An In-Depth Comparison
– Twin Cam 88 vs 96: Dual Cam Shootout (What’s Better?)
– Is The Twin Cam 96 A Good Motor? Yes and No (Here’s Why)
The Advancements of the Harley 103 Engine

Continuing the drive for performance enhancement, the introduction of the Harley 103 motor provided even more torque but truly shone when combined with targeted Harley Davidson engine upgrades. These engines came into their own with additional tweaks, such as updated cams and improved intake systems, amplifying the already impressive Harley Davidson engine sizes. Doctrines of reliability also evolved, addressing the cam tensioner issues of the past and ensuring each ride was as smooth as it was thrilling.
Compare more here:
– Harley 96 vs 103: What’s The Deal?
– Harley 96 vs 107: Performance, Upgrades, and More
– Harley 103 vs 107: Evolutionary Or Just A Step Backwards?
– Harley 103 vs 117: The Ultimate Comparison (Who Wins?)
Harley 88 vs 96 vs 103: Performance Across the Decades
As the chronicles of motorcycle legend unfurl, the Harley Davidson engine sizes have narratively powered through the roadmap of innovation. Beginning with the robust 88 cubic inch powerhouses, these engines set a precedent for unfailing performance, presenting an unwavering baseline for the Harley-Davidson breed. Adaptations like the 95 kit have become almost rites of passage for riders looking to bolster the prodigious legacy of their trusted machines.
The ascension to the bigger motor, from the 96 and 103 cubic inch engines, signifies the brand’s venturesome pursuit of more power and torque, providing a huge difference between the two. In the throes of friendly Harley Davidson comparison and roll-on duels, these larger engines demonstrate their might, particularly when whisked to life by higher-stage modification kits. It remains a point of pride that a fine-tuned 88 cubic inch engine, in a show of bravado, can still dance toe-to-toe with or even eclipse a stock 103, while a judiciously upgraded 96 might nimbly chase the shadow of a 103 during a tense top-gear acceleration.
Despite the advent of cam tensioner issues in early Twin Cam models, the resilience of these engines—across all sizes—stands testament to their Harley engine performance. With adept modifications, the primeval roar of immense power remains at the rider’s throttle-twist.
- 88 cubic inch engines preserve the spirit of seasoned performance, ripe for upgrades and custom tuning.
- 96 and 103 cubic inch engines echo the brand’s progressive ethos, offering enhanced stock power that scales with the rider’s ambition.
- The confluence of engine size and rider skill burgeons into a symphony of velocity, rewriting the odyssey of the ride.
Riders muse over the symphony of engines, finding kinship in the vibrations of an 88, or reveling in the brawn of a 96 or 103. The chorus of Harley-Davidson’s legacy, rich with the timbres of these engines, faithfully accompanies the personal journey of each rider seeking their definition of unadulterated horsepower.
Which Models Utilized These Twin Cammed Engines?
| Motorcycle Model | Years Produced | Engine Displacement |
|---|---|---|
| Dyna Series | 1999-2017 | 88ci (1450cc), 96ci (1584cc), 103ci (1690cc) |
| Touring Series | 1999-2016 | 88ci (1450cc), 96ci (1584cc), 103ci (1690cc) |
| Softail Series | 2000-2017 | 88ci (1450cc), 96ci (1584cc), 103ci (1690cc) |
| CVO Models | Various years | 103ci (1690cc) and other variants |
| Trike Models | Various years | 103ci (1690cc) |
| Fat Bob | 2008-2017 | 96ci (1584cc), 103ci (1690cc) |
| Switchback | 2012-2016 | 103ci (1690cc) |
Conclusion
In the journey of choosing the ultimate Harley-Davidson engine, be it the formidable 88, the robust 96, or the potent 103 cubic inches, the decision is deeply personal and varies with each rider’s pursuit of more power and performance. The nuanced differences between Harley 88, 96, and 103 offer distinct experiences to the discerning motorcyclist, each engine appealing to various aspects of riding, from torque delivery to the eagerness for upgrades. This Harley-Davidson engine comparison is more than a mere technical evaluation—it’s an integral part of defining one’s ride and road presence.
Choosing the Right Engine: What Matters Most
When it comes to fine-tuning for peak Harley–Davidson performance, the idiosyncrasies of the 88, 96, and 103 engines emerge, showing each their rightful place in the lineage of legendary rides. Adjustments and Harley engine upgrades can transform these motors to better align with individual riding styles and power needs. In this spectrum of customization, riders must weigh their expectations—seeking either the classic charm of the 88 or the contemporary thrust of the 103—against the backdrop of Harley engine specifications.
Maintaining Your Harley Engine for Longevity and Reliability
A steadfast commitment to maintenance guarantees the longevity and reliability that Harley-Davidson engines are known for. The renowned durability of these engines doesn’t stem from happenstance but through meticulous care and addressing issues—such as the tensioner challenges in the early Twin Cam models—with preemptive diligence. Mastery of one’s motorcycle extends beyond riding; it involves an understanding and a proactive approach to preserving its heart—the engine—ensuring it stands the test of time and adventure.